Return to Research projects |
Publications |
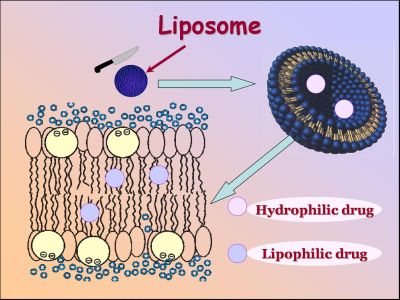
| Liposome-based drug nanocarriers | |
 |
Among a wide variety of drug nanocarriers liposome-based delivery systems are particularly attractive due to a number of advantages, such as biocompatibility, complete biodegradability, low toxicity, ability to carry both hydrophilic and lipophilic payloads and protect them from chemical degradation and transformation, increased therapeutic index of a drug, reduced side effects, etc. The physicochemical characteristics of liposomes (size, lamellarity, surface charge, pH- and thermosensitivity) can be readily manipulated. Furthermore, the possibility of bringing together therapeutic, targeting and imaging compounds makes liposomes an ideal candidate for producing nanocarriers with a number of coordinated specialized functions, optimum pharmacokinetic parameters and controlled drug release in the pathological zone in response to pH, temperature, photo or other stimuli. |
|
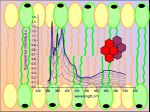
Development of liposomal carriers is heavily based on the evaluation of membrane-partitioning and bilayer-modifying properties of the drug. This is important not only for achieving maximum payload without compromising liposome stability, but also for prediction of therapeutic and toxic effects of a certain compound, because membrane interactions may prove critical for drug absorption, distribution, metabolism and elimination in an organism.
We are exploring membrane interactions of two types of drugs:
The studies of lanthanides are conducted in close cooperation with Prof. Todor Deligeorgiev, Dr. Alexey Vasilev and Prof. Nikolay Gadjev from Sofia University "St. Kliment Ohridski", Bulgaria. Membrane-associating and bilayer-modifying properties of the drugs are evaluated using absorption and fluorescence spectroscopy techniques. |
 |

|
 |
 |
 |
Return to Research projects |
Publications |